Kazan 2008
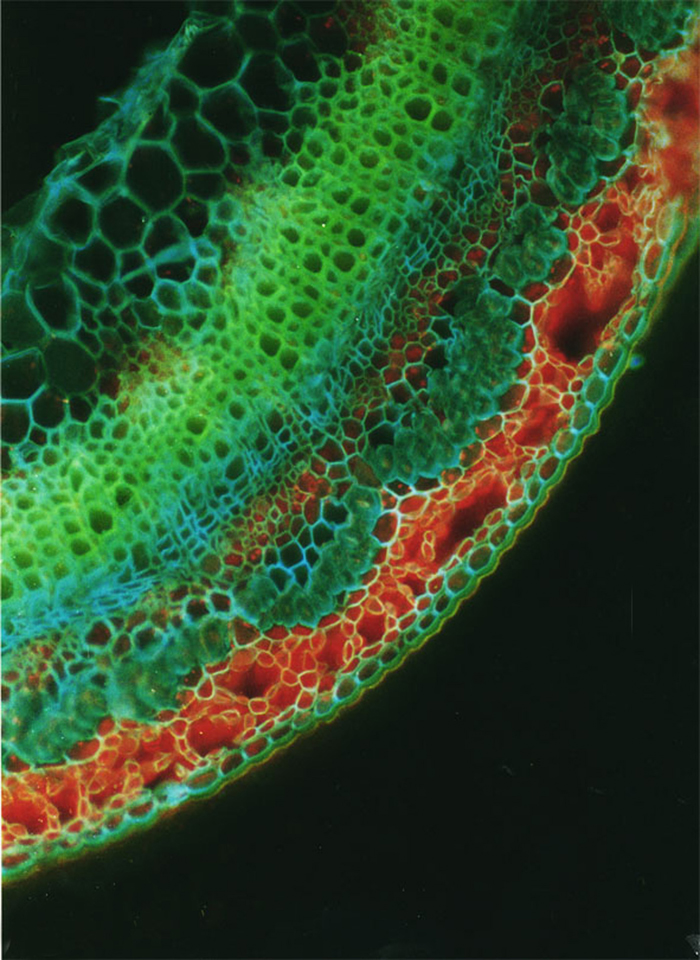
Free-hand cross-sections of flax stems stained with Cellufluor and viewed with broad-wavelength fluorescence detection. A representative flax plant at the fast-growing stage. Section taken 5 mm above the snap point. Срез стебля на уровне Т4, быстрый рост, Сеllufluor. Можно наблюдать флоэмные волокона, которые имеют толстую клеточную стенку. Масштаб: 40 мкм. Ув. 1280.
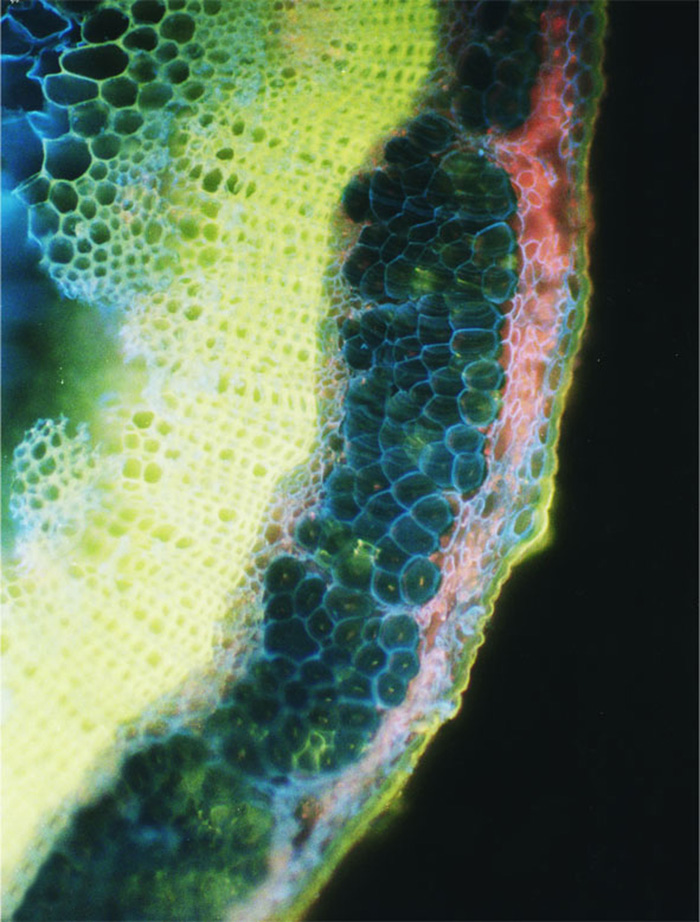
Section taken from the middle of the stem. Срез на уровне середины стебля льна-долгунца на стадии желтая спелость, Cellufluor. Масштаб: 40 мкм. Ув.1 280.
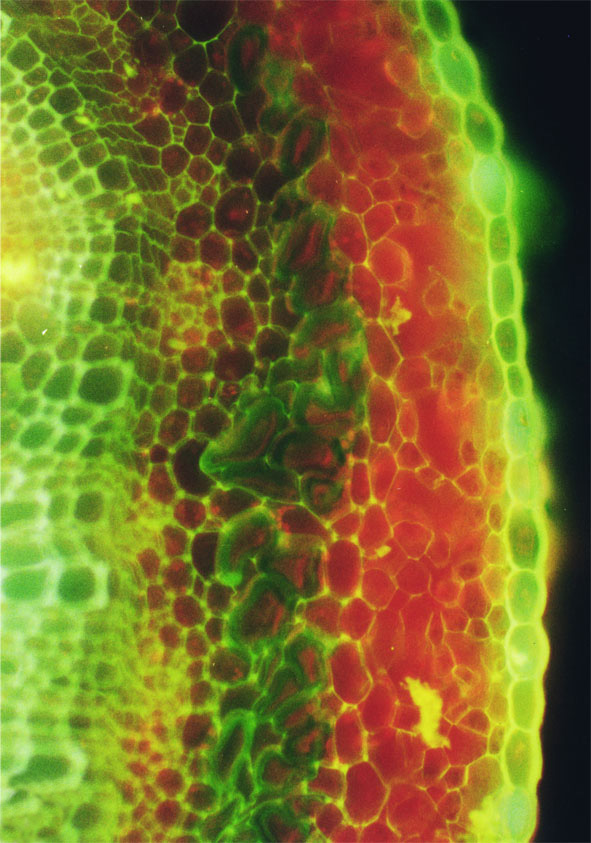
Срез стебля на уровне Т4, период быстрого роста, окрашивание СКП. Срединная пластинка большинства клеток флуоресцирует под УФ желтым цветом. Масштаб:40 мкм. Ув. 2 560.
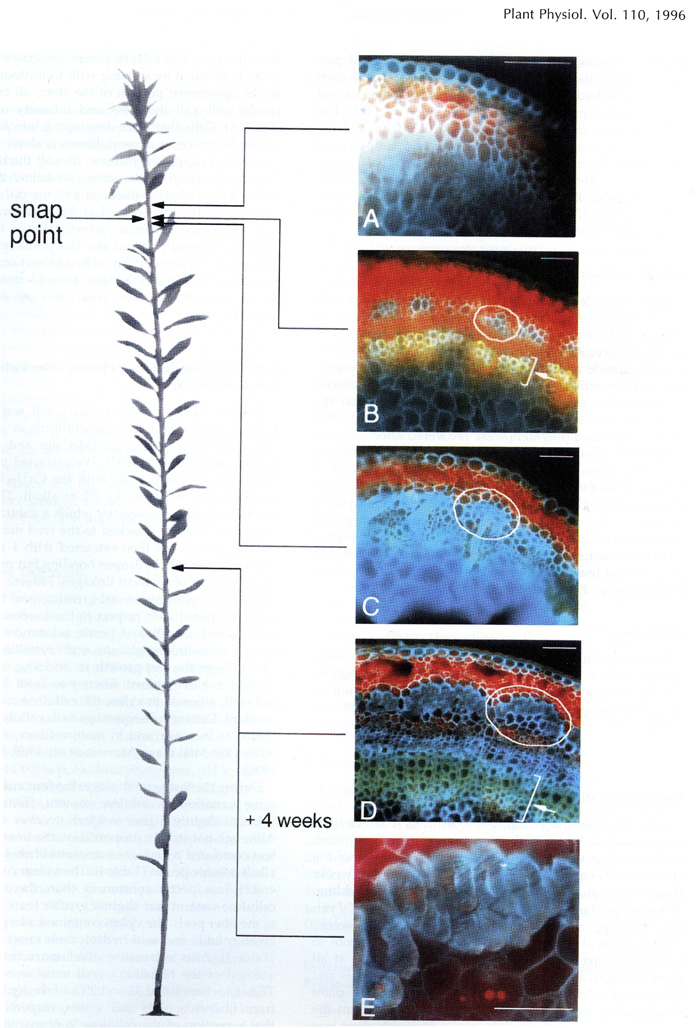
Free-hand cross-sections of flax stems stained with Cellufluor and viewed withbroad-wavelength fluorescence detection. A representative flax plant at the fast growing stage from which sections were taken is shown at left. A - Section taken 5 mm above the snap point; B - section taken 1 mm above the snap point; C - section taken 1 mm below the snap point; D - section taken from the middle of the stem; E - section taken from the middle of the stem at budding stage 4 weeks later. The intense blue Cellufluor fluorescence is localized in phloem fiber walls. A representative bundle of fibers is encircled in white, and arrows indicate xylem. For A through D, bar = 100 pm; for E, bar = 50 pm. The red color is from Chloroplast autofluorescence, and yellow is the autofluorescence of lignin, primarily in xylem (Gorshkova T.A., Wyatt S.E., Salnikov V.V., Gibeaut D.M., Ibragimov M.R., Lozovaya V.V., Carpita N.C. Cell wall polysaccharides of developing flax plants. Plant Physiol. 1996, v. 110, N 3, c. 721-729).
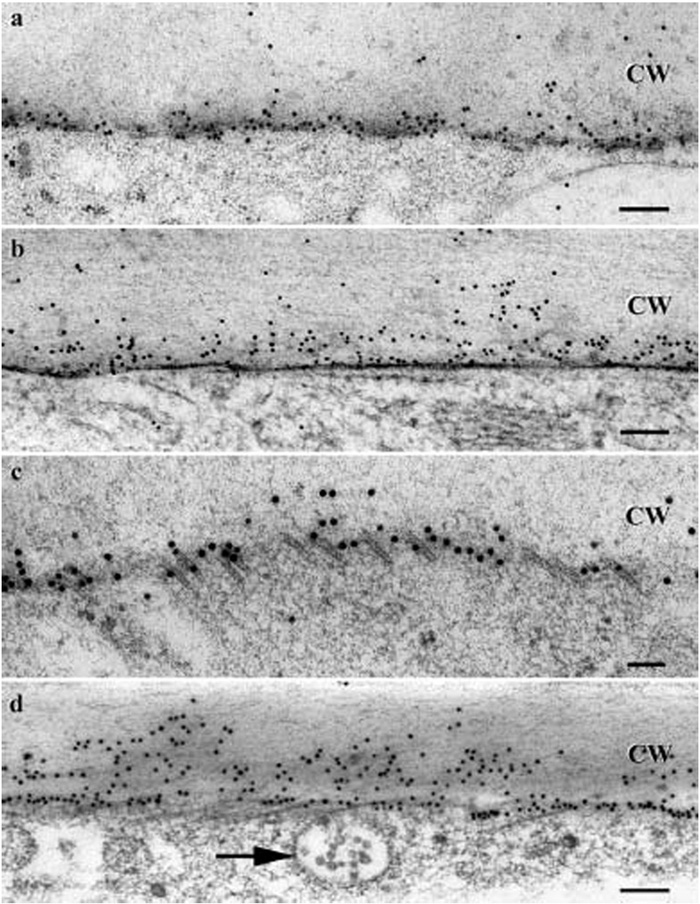
SuSy (Sucrose synthase) labeled with colloidal gold in cryofixed 24 DPA cotton fibers (freeze substitution in acetone only). a–c In planta fibers. a - SuSy labeling mainly near the plasma membrane. b - SuSy labeling near the plasma membrane and in the exoplasmic zone; note that this micrograph illustrates immunolabeling in the context of ice-damaged but still recognizable ultrastructure. c - SuSy labeling near the cortical microtubules, which are indicated by short open tubes near the juncture between the cytoplasm and the cell wall in this tangential section. d In a fiber from a cultured ovule, SuSy labeling was observed near the plasma membrane and in the exoplasmic zone.The arrow indicates a multivesicular body.CW - Secondary wall. Bars: 0.2 mm (Salnikov V., Grimson M., Seagull R., Haigler C. The localisation of sucrose synthase and callose in freeze substitution secondary- wall stage cotton fibers. Protoplasma, 2003, Jun; 221(3-4): P. 175-184).
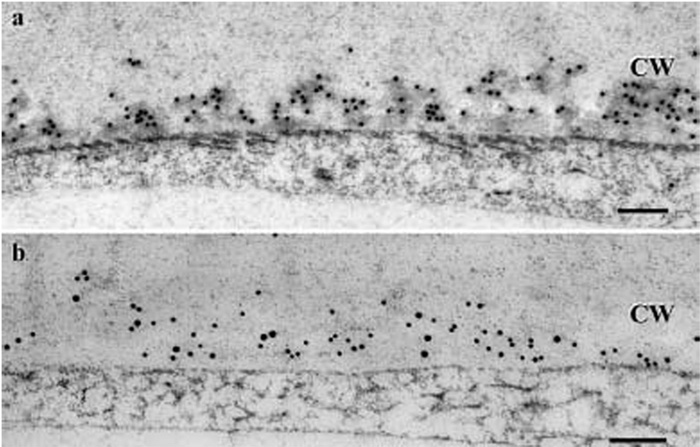
Cryofixed 24 DPA, in planta cotton fibers (freeze substitution in acetone only). a -Callose labeling in the exoplasmic zone; b - double labeling of callose (20 nm diameter gold) and SuSy (10 nm diameter gold) showed that the two antigens are codistributed within the exoplasmic zone. CW Secondary wall. Bar: 0.2 mm (Salnikov V., Grimson M., Seagull R., Haigler C. The localisation of sucrose synthase and callose in freeze substitution secondary- wall stage cotton fibers. Protoplasma, 2003, Jun; 221(3-4): P. 175-184).
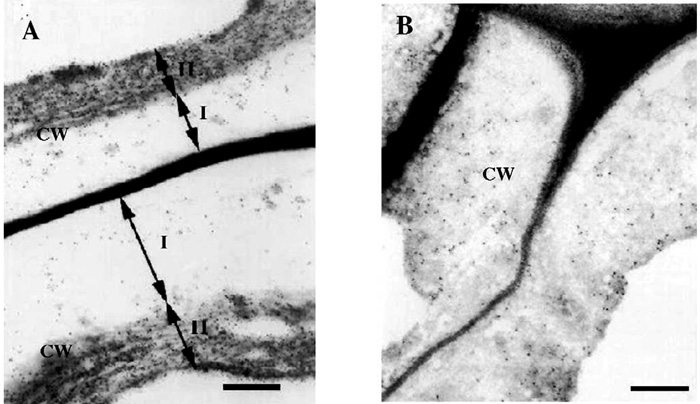
Immunogold labeling of flax bast fiber cell wall with LM5 monoclonal antibody: (A) without treatment and (B) treated with water. Scale bar - 0.5 µm (Gorshkova T. A., Chemikosova S. B., Salnikov V.V., Pavlencheva N. V., Stolle-Smits T., van Dam J.E.G. Occurrence of cell-specific galactan is coinciding with bast fibre development transition in flax. 2004, Ind. Crops and Prod., N18, P. 213-221).
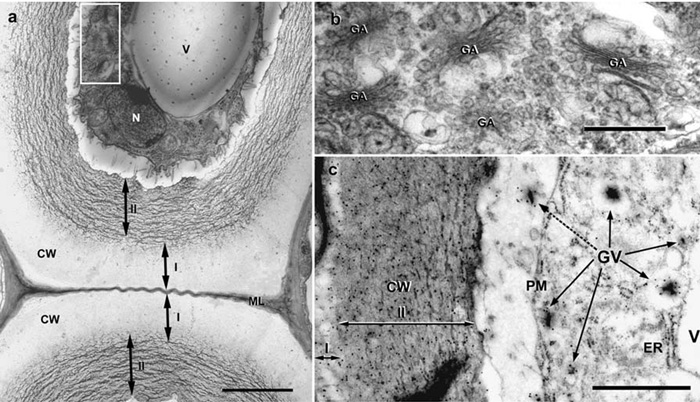
Ultrasructure of flax phloem fibers. (a) Fiber cells with two distinct cell wall layers at fast growth stage of flax plants. The white rectangle indicates the fiber cytoplasm part presented on Figure 2(b). Scale bar 2.5 mm. (b) Golgi apparatus (GA) and Golgi vesicles with electron-dense contents. Scale bar 0.5 mm. (c) The immunogold labeling (LM5 antibody) of b - (1→4) galactan in flax fiber. Labelingoccurred in cell wall (CW) and Golgi vesicles (GV, arrows). Golgi vesicle content in the periplasmic space (dotted arrow). Note the outer layer starting to form in secondary cell wall (I). Scale bar 1 mm. ER – endoplasmic reticulum, N – nucleus, PM – plasma membrane, V – vacuole, I – outer, II – inner layers of secondary cell wall (Gorshkova T., Ageeva M., Chemikosova S., Salnikov V. Tissue-specific processes during cell wall formation in flax fiber. Plant Biosystems. - 2005, V.1, P.88-92).
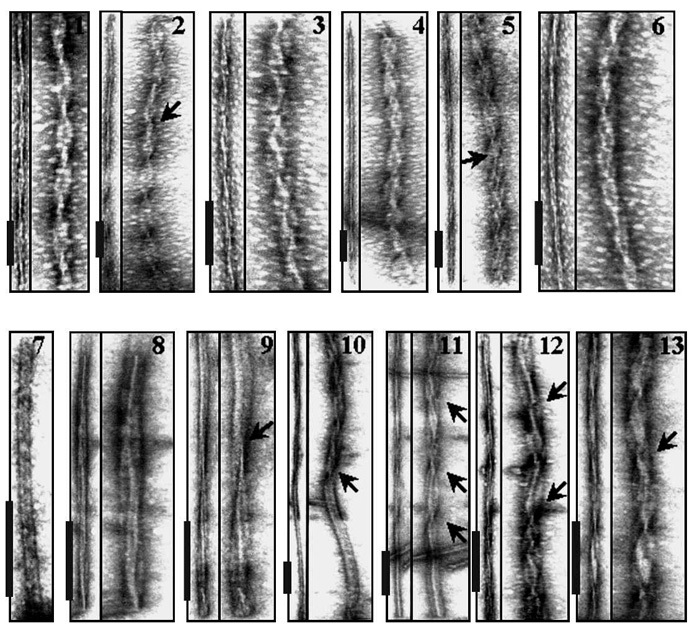
Gallery of negatively stained mature fibrils produced from Ha PrP (panels 1–6) and from Mo PrP (panels 7–13). The left panel in each pair displays actual electron micrographs, while the right panel corresponds to the same image extended perpendicular to the fibril axis to visualize the details in the intertwining pattern of individual fibrils. Arrows mark sites where the twisting pattern changes or switches to untwisted flat morphology. Scale bars are 0.2 mm. Mo and Ha full-length recombinant PrPs encompassing residues 23–230 and 23–231, respectively, were expressed, purified, and folded into the amyloid form as described earlier (Makarava N, Bocharova OV, Salnikov VV, Breydo L, Anderson M, Baskakov IV. Dichotomous versus palm-type mechanisms of lateral assembly of amyloid fibrils // Protein Sci. 2006 Jun; 15(6): P.1334-41).
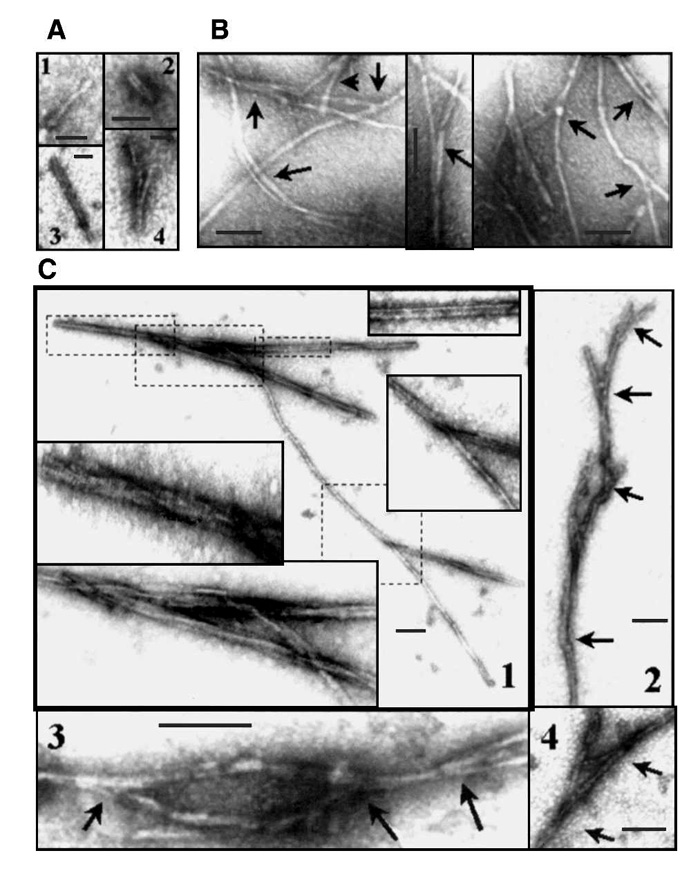
EM images of Mo PrP fibrils collected at early stages of assembly. Samples were taken at 20%–40% (A), 40%–60% (B), or 60%– 100% (C) of the lag phase. Scale bars are 50 nm in A, and 0.1 mm in B and C. Mo PrP fibrils display a dichotomous pattern of coalescence, where the ‘‘coalescence forks’’ are marked by arrows. Several events of hierarchical assembly observed within an individual fibril are shown on panels 1 and 2 in c. Inserts in panel 1 correspond to the areas marked with dashed lines and contain enlarged regions showing morphological details. At each time interval three aliquots were taken, and up to 10 EM images were collected from each sample and analyzed (Makarava N, Bocharova OV, Salnikov VV, Breydo L, Anderson M, Baskakov IV. Dichotomous versus palm-type mechanisms of lateral assembly of amyloid fibrils // Protein Sci. 2006 Jun; 15(6): P.1334-41).
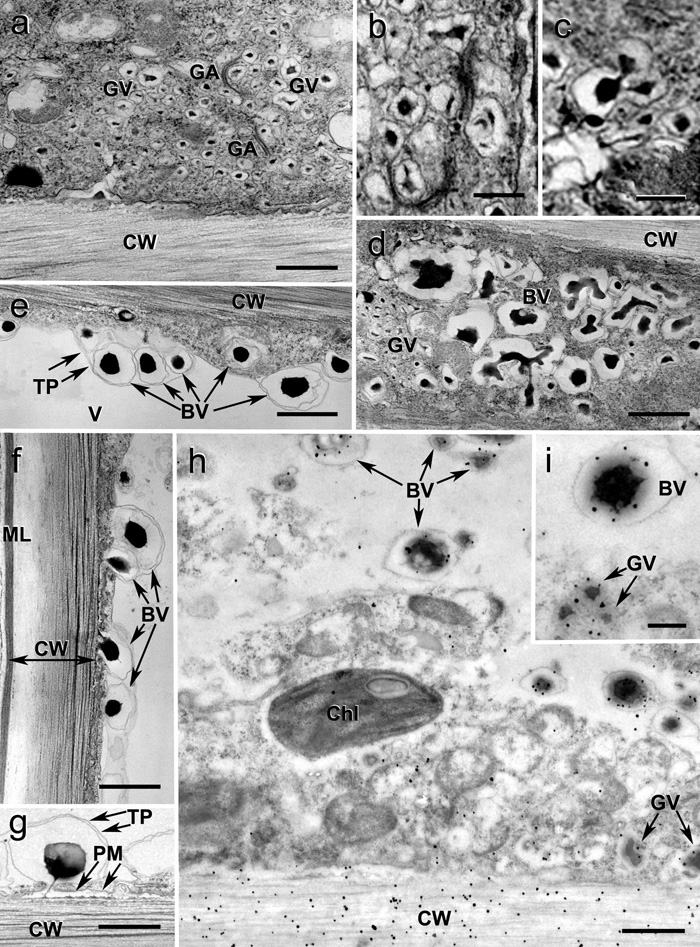
Bicolor vesicles and vacuoles in flax fiber cytoplasm during formation of gelatinous cell wall layers. а - Accumulation of specific (bicolor) vesicles in fiber cortical cytoplasm. b - Budding of bicolor vesicles from Golgi cisternae. c - Homofusion of bicolor Golgi vesicles into bicolor vacuoles. d - Homofusion of bicolor vacuoles. e - Invaginations of tonoplast with bicolor vacuoles. f - Fusion of bicolor vacuoles with the plasma membrane (arrows). G - “Syringe-like” squeezing of the dark content of a bicolor vacuole into the periplasm with formation of a dark stripe on the cell wall surface. h - Labeling of Golgi derivatives (arrow) and the inner layer of the secondary cell wall with LM5 antibody. i - Higher magnification of an individual bicolor vacuole labeled with LM5 antibody. BV - Bicolor vacuoles, Chl- chloroplast, CW - secondary cell wall, GA- Golgi apparatus, GV- Golgi vesicles, ML - middle lamella together with primary cell wall, V- central vacuole, PM - plasma membrane, TP - tonoplast. Bar: a, d, e, f, g - 1.0 μm; b, c, i - 0.2 μm (Salnikov VV, Ageeva MV, Gorshkova TA. Homofusion of Golgi secretory vesicles in flax phloem fibers during formation of the gelatinous secondary cell wall. Protoplasma. 2008 2008;233(3-4):269-73. Epub 2008 Sep 10).
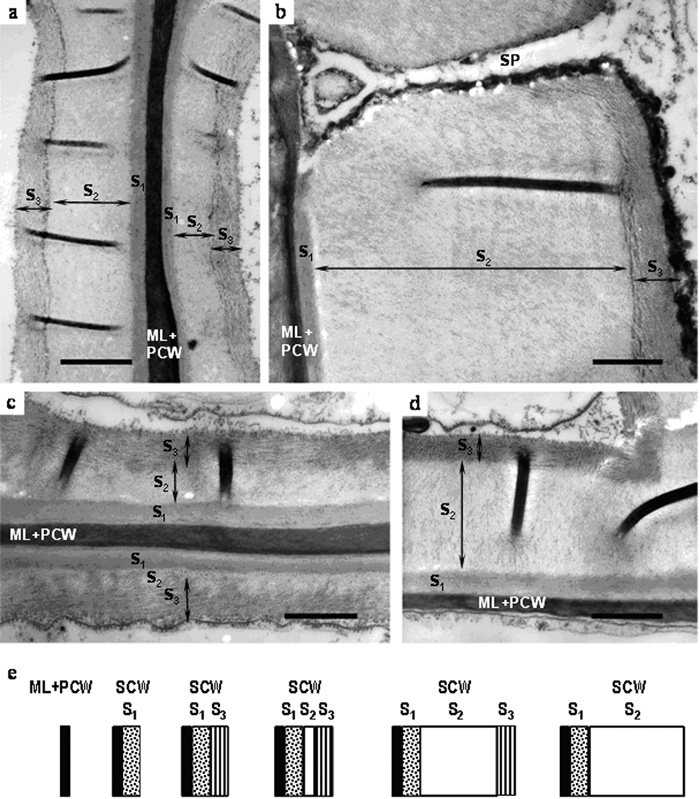
Deposition and remodeling of secondary cell wall in hemp fibers. (a) early development stage and (b) late development stage of primary fiber secondary cell wall formation; (c) early development stage and (d) late development stage of secondary fiber secondary cell wall formation; (e) scheme of sequential steps in deposition and remodeling of secondary cell wall layers in both primary and secondary hemp fibers. ML – middle lamellae; PCW – primary cell wall; S1, S2, S3 – secondary cell wall layers; SP – simple pore. Bar – 1.0 µm.
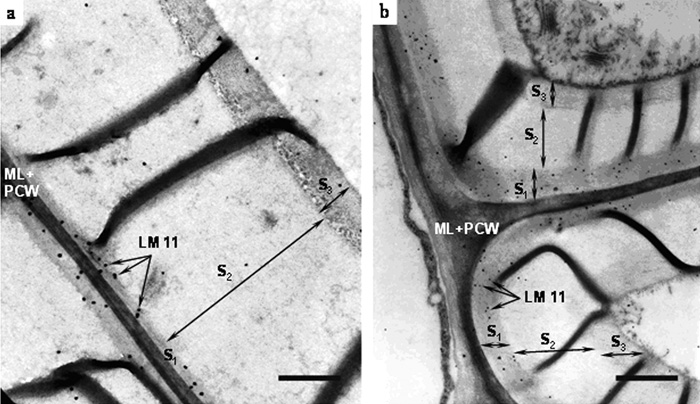
Immunogold labeling of (a) primary and (b) secondary hemp fibers with monoclonal antibody LM11. ML – middle lamellae; PCW – primary cell wall; S1, S2, S3 – secondary cell wall layers. Bar – 1.0 µm.

Baltimore 2005

Texas 2001

Kazan 2008

Kazan 2008

Kazan 2008

Kazan 2008


















